Zinc Oxide: The Mineral Powerhouse in Skincare and Sun Protection
Zinc Oxide: The Mineral Powerhouse in Skincare and Sun Protection
Exploring the UV benefits of this multitasking skin protectant
Zinc oxide is one of the most effective and multifunctional ingredients used in dermatology—and it’s also a star component in our Vivoderm Zinc Repairing Facial Cream. While this cream is not an FDA-registered sunscreen, it contains 30% Zinc Oxide, which offers significant natural UV protection and skincare benefits.
Let’s break down what makes zinc oxide such a powerful player in modern skincare and why it deserves a spot in your daily routine.
A Closer Look at Zinc Oxide
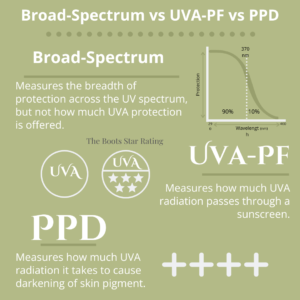
Zinc oxide is one of only two mineral (physical) sunscreen actives approved for use in the U.S. (the other being titanium dioxide). As a mineral UV filter, zinc oxide is recognized for its ability to provide broad-spectrum protection—shielding skin from both UVB and the full range of UVA rays (UVA I & II). This makes it the most complete UV filter available worldwide.
While the maximum allowed concentration in U.S. and EU sunscreens is 25%, Vivoderm’s cream uses 30% zinc oxide for its skin-soothing and protective properties—not as a regulated sunscreen, but as a natural shield and repair aid for compromised or sensitive skin.
How It Works: Absorption, Not Just Reflection
Zinc oxide is often described as a physical blocker that “reflects” UV light like a mirror. While that’s partly true, research shows that it primarily works by absorbing UV radiation and converting it to heat—just like chemical sunscreens. A 2016 study published in Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine confirmed this mechanism, debunking the myth that mineral filters only reflect light 1.
This ability to absorb UV while remaining gentle and non-irritating makes zinc oxide an ideal choice for sensitive skin and post-treatment care.
Mineral vs. Chemical Sunscreens: What’s the Difference?
Sunscreen filters are generally divided into two categories: mineral (physical) and chemical. The main distinction lies in how they interact with UV rays.
Mineral sunscreens, like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, sit on top of the skin and were traditionally thought to reflect UV rays. However, research has shown that they actually absorb most UV radiation and convert it to heat, much like their chemical counterparts. These filters are inorganic compounds and are less likely to irritate the skin, making them ideal for sensitive or reactive skin types.
Chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, use organic compounds like avobenzone, octinoxate, and octocrylene. These filters penetrate the upper layers of the skin and absorb UV rays, then disperse them as heat. While often more cosmetically elegant (they tend to go on clear and feel lighter), some chemical filters can cause irritation or allergic reactions in certain individuals.
For many, the choice between mineral and chemical sunscreen comes down to skin sensitivity, aesthetic preferences, and level of UV protection needed. Zinc oxide, as a mineral filter, stands out because it provides broad-spectrum coverage, is non-irritating, and is recognized as safe and effective by global health authorities.
Let me know if you’d like to emphasize this comparison more visually, like with a table or bulleted list!
Skin-Calming and Protective Perks

Man Applying Protective Sunscreen On Woman Tanned Shoulder At Beach.
Beyond sun defense, zinc oxide is a skin protectant officially recognized by the FDA. You’ll find it in:
- Diaper rash creams
- Calamine lotion
- Anti-itch and healing balms
It offers astringent properties that help calm redness, reduce oiliness, and support healing—especially helpful for acne-prone or irritated skin. These qualities are key benefits of our Zinc Repairing Facial Cream, which uses zinc oxide not just for its UV filtering ability but for its reparative action on dry, inflamed, or damaged skin.
The White Cast Tradeoff
The downside? Higher concentrations of zinc oxide can lead to the infamous white cast—a chalky residue that’s more noticeable on deeper skin tones. That’s why many cosmetic formulators opt for nano zinc oxide, which helps reduce this effect. However, concerns about nanoparticles have led to ongoing discussions about their safety (though current data does not show significant risk).
Is Zinc Oxide Safe?
Yes. In fact, zinc oxide is one of only two sunscreen ingredients classified as GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) by the FDA 2. It’s unlikely to trigger allergic reactions, unlike some chemical filters, and its long-standing use in dermatological products makes it a trusted option for daily skin support.
Final Thoughts
While Vivoderm Zinc Repairing Facial Cream is not a sunscreen, its 30% zinc oxide content provides a layer of natural environmental defense and skin protection. Think of it as a daily recovery shield—especially beneficial for sensitive, acne-prone, or post-procedure skin.
For full sun protection, we recommend layering your skincare with a broad-spectrum SPF, or choosing a hybrid sunscreen that combines both mineral and chemical filters for optimal protection and wearability.
SOURCES
Ekstein, Samuel F., and Sara Hylwa. “Sunscreens: A Review of UV Filters and Their Allergic Potential.” Dermatitis, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1097/der.0000000000000963
Footnotes
- Cole, Curtis, et al. “Metal Oxide Sunscreens Protect Skin by Absorption, Not by Reflection or Scattering.” Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine, vol. 32, no. 1, 2015, pp. 5–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/phpp.12214 ↩
- FDA. “Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS).” U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Oct. 2023. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/generally-recognized-safe-gras ↩